Thursday, February 27, 2014
Wednesday, February 19, 2014
Compound Interest Formula
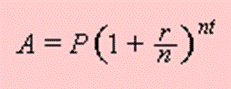
P: Principal , amount o money borrowed
R: Rate of interest ( written as a decimal
N: Number of times compounded
Annually: 1
Semiannually: 2
Monthly: 12
Quarterly : 4
T: Time (always in years)
Things to Remember :
- There are 52 weeks in a year
- There are 365 days in a year
- There are 4 quarters in a year
Example: An amount of $1,500 is deposited in a bank paying an annual interest rate of 4.3%, compounded quarterly. What is the balance after 6 years?
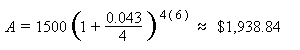
General Forms of a Sequence
- Sequence: a list of numbers
- Finite Sequence: a sequence that ends
- Infinite Sequence: a sequence that keeps going

Types of Sequences
- Arithmetic Sequence: have a common difference and you find it by subtracting the last number from the next and so on.
Example: 1,4,7,10,13
13-10 =3
10-7=3
7-4=3
4-1=3
So the common difference is 3 which is represented as d=3
The formula that represents arithmetic sequences is:

- Geometric Sequences: have a common ration and you can find it by dividing the last number by the next number.
Example : 4,24,144,864....
864/144=6
144/24=6
24/4=6
So the common ration is 6 represented as r=6
The formula that represents geometric sequences :
To find a specific term in a sequence you just plug that number into the An
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
