Wednesday, April 30, 2014
Friday, April 18, 2014
Wednesday, April 2, 2014
Review 1
These are the questions I missed:
I missed this because I didn't round to the nearest meter
I missed this because I didn't find the smallest are
I missed this because i didn't find the smallest volume
Tuesday, April 1, 2014
Wednesday, March 19, 2014
Linear Programming
Vertices:
|
||||||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C=3x+4y
|
|||||||
x ≥
0
y ≥
0
x + y ≤ 5
|
C=24
|
C=0
|
C=18
|
|||||
Vertices
| (-15,0) | (0,6) | (5,0) | |||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C= -2x+5y
|
|||||||
x≤5
y≥4
-2x+5y≤30
|
C=30
|
C=30
|
C=-10
|
|||||
Vertices:
|
||||||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C=7x+3y
|
|||||||
x≥1
y≥2
6x+4y≤38
|
C=31
|
C=13
|
C= 42
|
|||||
|
|
||||||||
Vertices:
|
(0,8)
|
(0,4)
|
(6,8)
|
|||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: 4x+6y
|
|||||||
y≥0
y≤8
-2x+3y≥12
|
C=48
|
C=24
|
C=72
|
|||||
Vertices:
|
(2,3)
|
|||||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C=8x+7y
|
|||||||
x ≥
0
y ≥
0
4x + 4y ≤ 20
x+2y ≤8
|
C=37
|
|||||||
Monday, March 10, 2014
Tuesday, March 4, 2014
Graphing Exponential Growth/ Decay
Formula : Y=a*b x –h +K

- Domain : (-∞,∞) - All Real Numbers
- Range : y >k - a is positive
y< k - a is negative
- Asymptote : y=k
- H= left/right (opposite)
- K= up/ down
- A= Multiplier
a >1 = stretch
0<a<1 = compression

a< 0 (negative) = flip over x axis
- B= base
b>1 = Growth (always increasing)
0<b<1 = Decay ( always decreasing)
Thursday, February 27, 2014
Wednesday, February 19, 2014
Compound Interest Formula
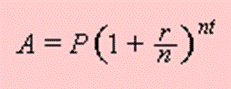
P: Principal , amount o money borrowed
R: Rate of interest ( written as a decimal
N: Number of times compounded
Annually: 1
Semiannually: 2
Monthly: 12
Quarterly : 4
T: Time (always in years)
Things to Remember :
- There are 52 weeks in a year
- There are 365 days in a year
- There are 4 quarters in a year
Example: An amount of $1,500 is deposited in a bank paying an annual interest rate of 4.3%, compounded quarterly. What is the balance after 6 years?
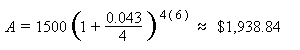
General Forms of a Sequence
- Sequence: a list of numbers
- Finite Sequence: a sequence that ends
- Infinite Sequence: a sequence that keeps going

Types of Sequences
- Arithmetic Sequence: have a common difference and you find it by subtracting the last number from the next and so on.
Example: 1,4,7,10,13
13-10 =3
10-7=3
7-4=3
4-1=3
So the common difference is 3 which is represented as d=3
The formula that represents arithmetic sequences is:

- Geometric Sequences: have a common ration and you can find it by dividing the last number by the next number.
Example : 4,24,144,864....
864/144=6
144/24=6
24/4=6
So the common ration is 6 represented as r=6
The formula that represents geometric sequences :
To find a specific term in a sequence you just plug that number into the An
Wednesday, January 15, 2014
Characteristics & Traits
- Domain : x values, describes a graph as it moves from left to right.
- Range: y values, describe a graph as it goes up and down.
- End Behavior: describes what happens on both ends.
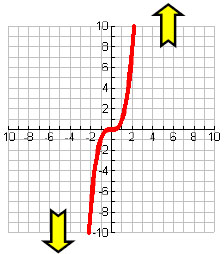
- Absolute Max/ Min: lowest/ highest point
- Local Max/Min: more than one highest or lowest point

- Interval of Increase: what happens to y values as you move along x axis.
- Interval of Decrease : describe what happens to the graph as you move left ans right on x axis.
- X Intercept: (a,0)
- Y Intercept : (0,b)
-

- Symmetry:
- Even: symmetric about the y axis
- Odd: rotational symmetry about origin
- Neither: None
- Asymptotes: imaginary line that a graph gets closer to, but never touches
- Function: passes vertical line test
 This picture does not pass vertical line test, so it is not a function
This picture does not pass vertical line test, so it is not a function- One to One: passes horizontal line test
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
















